
As a young man, Benjamin Franklin drew up a “plan for attaining moral perfection” based on a list of 13 virtues. Half a century later he credited the plan for much of his success in life. In this episode of the Futility Closet podcast we’ll explore Franklin’s self-improvement plan and find out which vices gave him the most trouble.
We’ll also learn how activist Natan Sharansky used chess to stay sane in Soviet prisons and puzzle over why the Pentagon has so many bathrooms.
Sources for our segment on Benjamin Franklin’s 13 virtues:
Benjamin Franklin, Autobiography, 1791.
Gordon S. Wood, The Americanization of Benjamin Franklin, 2005.
Dinah Birch, ed., The Oxford Companion to English Literature, 2009.
Here’s Franklin’s list of virtues:
- Temperance. Eat not to dullness; drink not to elevation.
- Silence. Speak not but what may benefit others or yourself; avoid trifling conversation.
- Order. Let all your things have their places; let each part of your business have its time.
- Resolution. Resolve to perform what you ought; perform without fail what you resolve.
- Frugality. Make no expense but to do good to others or yourself; i.e., waste nothing.
- Industry. Lose no time; be always employ’d in something useful; cut off all unnecessary actions.
- Sincerity. Use no hurtful deceit; think innocently and justly; and, if you speak, speak accordingly.
- Justice. Wrong none by doing injuries, or omitting the benefits that are your duty.
- Moderation. Avoid extreams; forbear resenting injuries so much as you think they deserve.
- Cleanliness. Tolerate no uncleanliness in body, cloaths, or habitation.
- Tranquillity. Be not disturbed at trifles, or at accidents common or unavoidable.
- Chastity. Rarely use venery but for health or offspring, never to dullness, weakness, or the injury of your own or another’s peace or reputation.
- Humility. Imitate Jesus and Socrates.
And here’s a sample page from his “little book”:
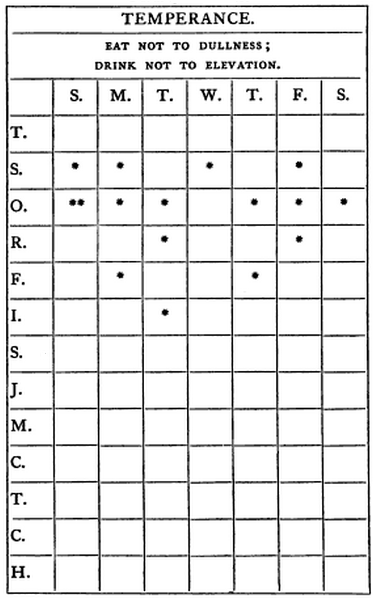
Related: As an exercise in penmanship, the teenage George Washington copied out “110 rules of civility and decent behavior in company and conversation,” and Thomas Jefferson once sent a “decalogue of canons for observation in practical life” to the new father of a baby boy.
Listener mail: Human rights activist Natan Sharansky’s use of mental chess to keep himself sane in Soviet prisons is detailed in his 1988 memoir Fear No Evil and in this BBC News Magazine article.
Greg’s research queries:
The authority on jumping up steps at Trinity College, Cambridge, seems to be G.M. Trevelyan, who became Master there in 1940. In his Trinity College: An Historical Sketch (1972), he writes:
It is a well-authenticated Trinity tradition that Whewell, when Master, jumped up the hall steps at one leap, a feat that is very seldom accomplished even by youthful athletes. Sir George Young told his son Geoffrey Young that he had actually witnessed this performance; Sir George said that the master, in cap and gown, found some undergraduates trying in vain to accomplish the feat. He clapped his cap firmly on his head, took the run, and reached the top of the steps at one bound.
In a letter to the Times on March 16, 1944, he writes, “On a recent visit to Cambridge, General Montgomery, on entering the Great Court at this college, pointed to the hall steps and said to me, ‘Those were the steps my father jumped up at one bound.’ The general’s father, Henry Hutchinson Montgomery, afterwards Bishop, was an undergraduate at Trinity from 1866 to 1870. He came here from Dr Butler’s Harrow with a great reputation as a runner and jumper.”
He adds, “Now we have a fully authenticated case of which I had not heard. Bishop Montgomery himself told his son the general, and the story was often told in the family. The general has asked me to send the facts to you in the hope that publication may elicit further facts.” I don’t know whether he ever received any.
As far as I can tell, Swiss criminologist Karl-Ludwig Kunz’s essay “Criminal Policy in Duckburg” was published only in a 2009 collection titled Images of Crime 3: Representations of Crime and the Criminal, which I can’t seem to get my hands on. The fullest discussion I’ve been able to find in English is this brief 1998 article from the Independent.
The program to distribute bananas to Icelandic children in 1952 is mentioned in science writer Willy Ley’s 1954 book Engineers’ Dreams.
The credit “Diversions by Irving Schwartz” in the 1966 movie The Sand Pebbles is mentioned (but not really explained) in this 2007 Telegram obituary of character actor Joseph di Reda.
MIT historian T.F. Peterson’s 2003 book Nightwork: A History of Hacks and Pranks at MIT says that the legend IHTFP (“I hate this f—ing place”) “has been unofficially documented in both the U.S. Air Force and at MIT as far back as the 1950s.” This MIT page traces it as far back as 1960 and gives dozens of euphemistic variants.
This week’s lateral thinking puzzle was submitted by listener Paul Kapp.
You can listen using the player above, download this episode directly, or subscribe on iTunes or via the RSS feed at http://feedpress.me/futilitycloset.
Please consider becoming a patron of Futility Closet — on our Patreon page you can pledge any amount per episode, and all contributions are greatly appreciated. You can change or cancel your pledge at any time, and we’ve set up some rewards to help thank you for your support.
You can also make a one-time donation via the Donate button in the sidebar of the Futility Closet website.
Many thanks to Doug Ross for the music in this episode.
If you have any questions or comments you can reach us at podcast@futilitycloset.com. Thanks for listening!
