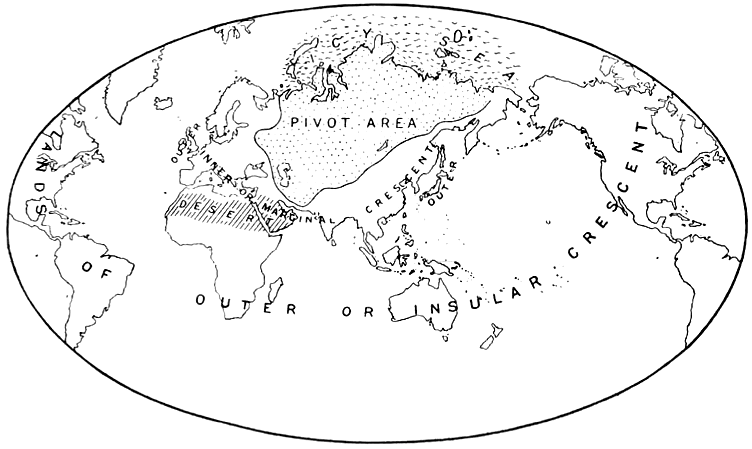
English geographer Halford Mackinder’s 1914 paper “The Geographical Pivot of History” helped to found the study of geopolitics. In it, he described his Heartland Theory, in which the world’s land surface was divided into the “World-Island,” meaning Europe, Asia, and Africa; the “offshore islands,” including Britain and Japan; and the “outlying islands,” including the continents of North America, South America, and Australia. At the world’s center lies the Heartland, stretching from the Volga to the Yangtze and from the Himalayas to the Arctic.
In 1919 he reduced his theory to three startlingly stark statements:
Who rules East Europe commands the Heartland.
Who rules the Heartland commands the World Island.
Who rules the World Island commands the World.
He thought the “pivot area” was impregnable to attack by sea and thus capable of building a land power that could conquer the world.
“No mere academic theoretician, Mackinder injected his Heartland thesis into the 1919 Paris Peace Conference that followed World War I,” write Mark Monmonier and George Schnell in Map Appreciation. “He recommended buffer states in Eastern Europe to prevent any nation(s) from gaining control of the Heartland, especially through a German-Soviet alliance. The conference’s subsequent creation of independent states from territories that had been parts of Austria-Hungary, Germany, or Russia varied little from Mackinder’s proposal and included Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania (along the Baltic Sea) and Poland, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia (extending from the Baltic to the Adriatic).”
