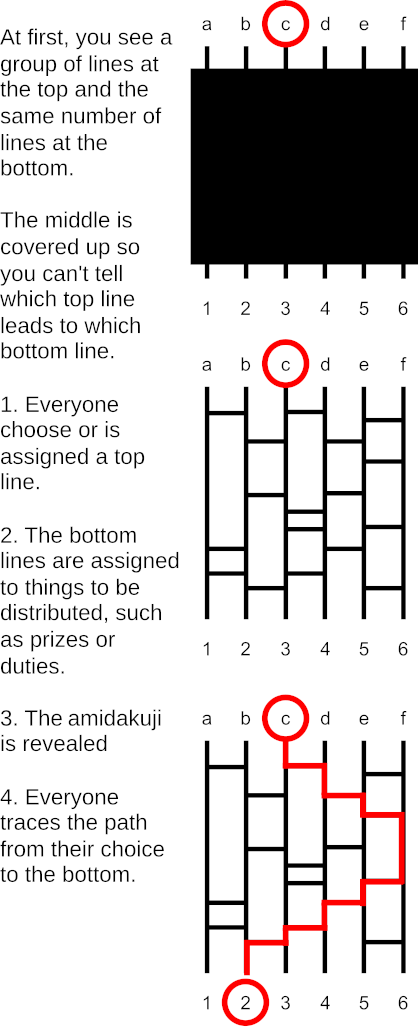
Ghost leg is a method of establishing random pairings between any two sets of equal size. For example, it might be used to assign chores randomly to a group of people. The names of the participants are listed across the top of the diagram and the chores across the bottom, and a vertical line is drawn connecting each name to the chore below it. Then the names are concealed and each participant adds a “leg” to the diagram. A leg is a segment that connects two adjacent vertical lines (it must not touch any other horizontal line).
When the legs have been drawn, the names are revealed and a path drawn from each name to the bottom of the diagram. Each path must follow each leg that it encounters, jumping to the adjacent vertical line and continuing downward. When it reaches a chore at the bottom, it establishes a link between a name and a chore.
The benefit of this method is that it will work for groups of any size, reliably establishing a 1:1 correspondence between their elements. And it will work no matter how many horizontal lines are added. In Japanese it’s known as amidakuji.