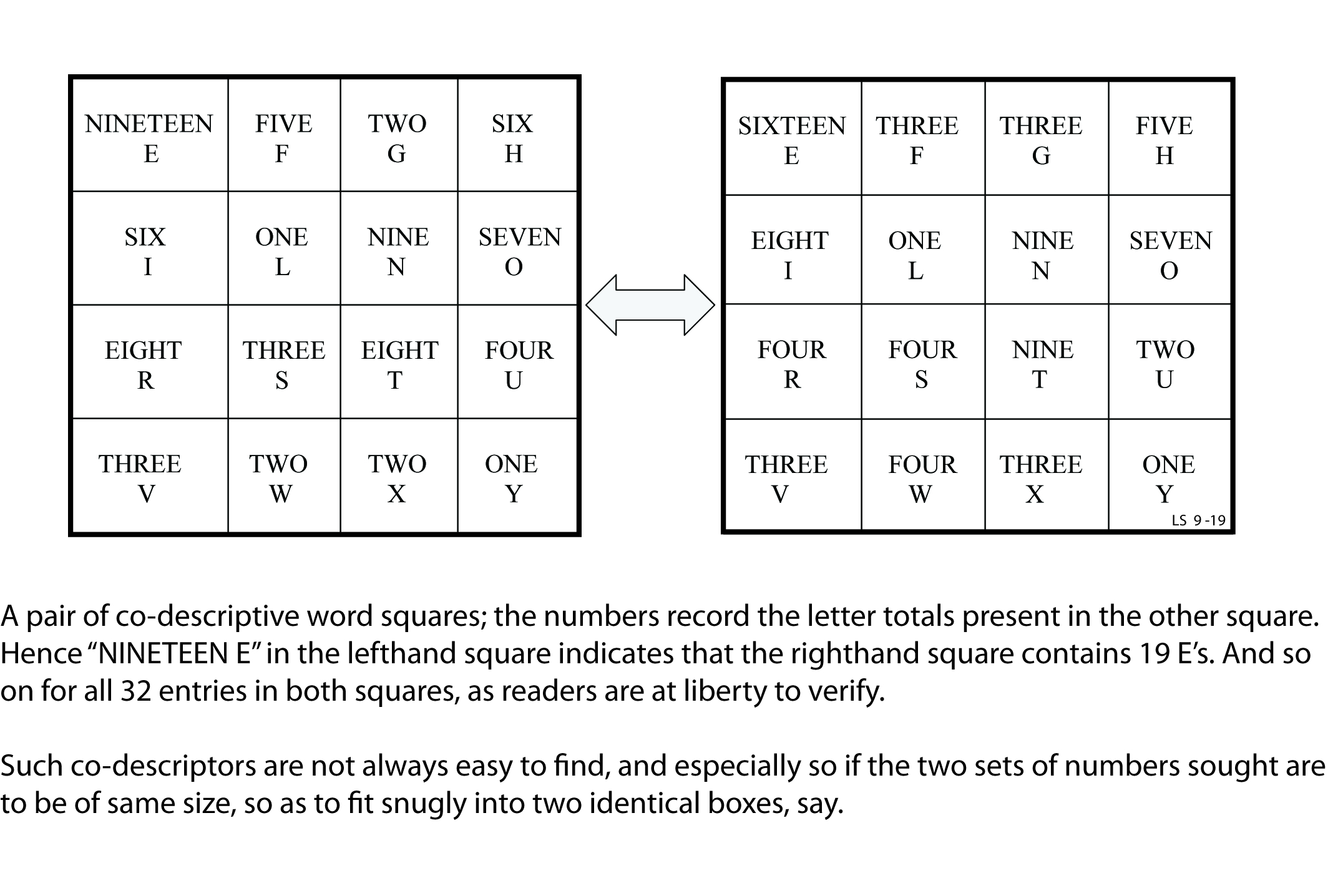
Demetri Martin composed this palindromic poem as part of a project for a fractal geometry class at Yale in spring 1993. The first two and last two lines are palindromes, the middle line (“Be still if I fill its ebb”) minus its last letter is a palindrome, and the entire poem is a palindrome:
Dammit I’m mad
Evil is a deed as I live.
God, am I reviled?
I rise, my bed on a sun, I melt.
To be not one man emanating is sad. I piss.
Alas it is so late. Who stops to help? Man, it is hot.
I’m in it.
I tell.
I am not a devil.
I level “Mad Dog”.
Ah, say burning is as a deified gulp
in my halo of a mired rum tin.
I erase many men. Oh, to be man, a sin.
Is evil in a clam? In a trap?
No. It is open.
On it I was stuck.
Rats peed on hope.
Elsewhere dips a web.
Be still if I fill its ebb.
Ew, a spider … eh?
We sleep.
Oh no!
Deep, stark cuts saw it in one position.
Part animal, can I live? Sin is a name.
Both, one … my names are in it. Murder?
I’m a fool. A hymn I plug,
Deified as a sign in ruby ash – a Goddam level I lived at.
On mail let it in. I’m it.
Oh, sit in ample hot spots.
Oh, wet!
A loss it is alas (sip). I’d assign it a name.
Name not one bottle minus an ode by me:
“Sir, I deliver. I’m a dog.”
Evil is a deed as I live.
Dammit I’m mad.