
“When anyone asks me how I can best describe my experience in nearly 40 years at sea, I merely say uneventful.” — Edward Smith, captain of the Titanic, in 1907

“When anyone asks me how I can best describe my experience in nearly 40 years at sea, I merely say uneventful.” — Edward Smith, captain of the Titanic, in 1907

More maxims of La Rochefoucauld:
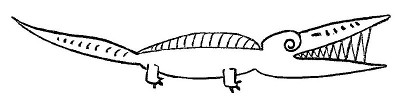
I give you now Professor Twist
A conscientious scientist.
Trustees exclaimed “He never bungles,”
And sent him off to distant jungles.
Camped by a tropic riverside,
One day he missed his loving bride.
She had, the guide informed him later,
Been eaten by an alligator.
Professor Twist could not but smile.
“You mean,” he said, “a crocodile.”
— Ogden Nash
(Thanks, Steve.)
English essayist A.C. Benson had rich, elaborate dreams, a trait common in his family. “Sometimes they would be processions and high ceremonies, diversified by the intervention of old Eton friends, who would whisper dark words more suo during some strange liturgy,” recalled his friend Geoffrey Madan. “Sometimes the distant past would rush upon him and old ecclesiastics, summoned up from the mists of Addington, became involved with him in situations of infinite absurdity; sometimes it would be oneself with whom the drama was played, till its recital at breakfast made one helpless with laughter.”
From one dream he awoke recalling only a strange epigram, “The riddle of life is solved by gliding, and not sliding.” On another morning he found that he had scribbled down these lines in the middle of the night:
A bold and cheerful company of Ogres, Ghosts, and Ghouls
Attacked and smashed to little bits the City of Tomfools:
The Tomfools sailed to Araby, and raised another state;
I can’t say how refined they were, and how considerate.
And now in High Tomfoolery they’re very fond of telling
What an almighty hash the ghosts made of their former dwelling;
They chaunt their great deliverance: they teach and preach and say
How good it was of God to take their former pride away.
He composed his poem “The Phoenix” entirely in his sleep. “I dreamed the whole poem in a dream, in 1894, I think, and wrote it down in the middle of the night on a scrap of paper by my bedside,” he wrote. “It is a lyric of a style which I have never attempted before or since. … I really can offer no explanation either of the idea of the poem or its interpretation. It came to me so (apparently) without any definite volition of my own that I don’t profess to understand or to be able to interpret the symbolism.”
By feathers green, across Casbeen,
The pilgrims track the Phoenix flown,
By gems he strewed in waste and wood
And jewelled plumes at random thrown.
Till wandering far, by moon and star,
They stand beside the fruitful pyre,
Whence breaking bright with sanguine light,
The impulsive bird forgets his sire.
Those ashes shine like ruby wine,
Like bag of Tyrian murex spilt;
The claw, the jowl of the flying fowl
Are with the glorious anguish gilt.
So rare the light, so rich the sight,
Those pilgrim men, on profit bent,
Drop hands and eyes and merchandise,
And are with gazing most content.
Madan added, “I have preserved in one of his letters the concluding stanza which he wrote in waking hours to round it off, but omitted later on the advice of a friend who felt it to be ‘incongruous’; this pleased him very much indeed.”
(From “A Later Friendship,” by Geoffrey Madan, in Arthur Christopher Benson as Seen by Some Friends, 1925.)
cultrivorous
adj. devouring knives
In June 1799, having watched a French mountebank pretend to swallow clasped knives, 23-year-old American sailor John Cummings boasted that he could do the same, and “after drinking freely” he proceeded to swallow his own pocketknife and three others offered by his friends.
Thus began a memorable career. According to George Budd in the Medical Times & Gazette, Cummings recounted his exploit in Boston six years later and was immediately challenged to repeat it. He swallowed six more knives, and an additional eight the following morning, “so that he had swallowed a knife for every day that the month was old.”
Nine months later, again inebriated, he made the same boast in England and swallowed five knives on Dec. 4 and nine clasp knives on Dec. 5 (plus, he was told, another four that he was too drunk to remember).
Through the next four years, in great pain and continually vomiting, Cummings applied to a number of doctors, at least one of whom dismissed his story as incredible. But when he died finally in March 1809, his stomach was opened and “a great many portions of blades, knife-springs, and handles were found in it, and were carefully collected for the museum at Guy’s Hospital, in which they are now preserved,” Budd notes — Cummings’ contribution to medical science.
After taking part in the attack on Pearl Harbor, Japanese fighter pilot Shigenori Nishikaichi crash-landed on the isolated Hawaiian island of Niihau. In this episode of the Futility Closet podcast we’ll recount the six days of escalating drama that unfolded between the desperate pilot and the terrified islanders.
We’ll also hear a list of open questions from Greg’s research and puzzle over why a man can’t sell a solid gold letter opener.
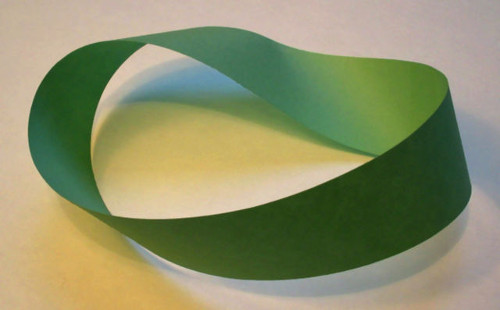
Gabriel Josipovici’s 1974 short story “Mobius the Stripper” is subtitled “A Topological Exercise.” The text is written in two strips, which tell two ostensibly different stories.
The first strip tells the story of Mobius, a man of uncertain origin who feels a metaphysical need to strip, “to take off what society has put on me” and discover his true self. He takes a job at a London club, where he talks as he performs and feels his essential self emerging. In the end, though, he comes to an existential crisis, unable to find any ultimate meaning, and shoots himself in his room to provide “an example to all.”
The second strip describes the troubles of an unnamed writer who shuts the world away, eager to write something new but overcome with writer’s block and intimidated by the writers of the past. His friend Jenny urges him to see a stripper named Mobius. “It’ll change your ideas,” she says. “Give it a break and you’ll all of a sudden see the light.” In the end, desperate to overcome the block, he begins to write a story about Mobius, whom he has never seen. “Perhaps it was only one story, arbitrary, incomplete, but suddenly I knew that it would make its own necessity and in the process give me back my lost self.”
If these tales are written on either side of a strip of paper, and one end of the strip is given a half-turn and then attached to the other, they create one unending story in which Mobius’ example frees the writer, who in his story gives new fictional depth to Mobius’ struggle, which lends it greater meaning and inspiration, and so on. Mobius is described differently in the two stories, suggesting that the Mobius of the first story is largely an invention of the writer in the second story. So where does the inspiration come from?

In 1890 the editor of the New York World invited Mark Twain to offer a message of holiday goodwill to its readers. He sent this:
It is my heart-warm and world-embracing Christmas hope and aspiration that all of us — the high, the low, the rich, the poor, the admired, the despised, the loved, the hated, the civilized, the savage — may eventually be gathered together in a heaven of everlasting rest and peace and bliss — except the inventor of the telephone.
Mark Twain
Hartford, Dec. 23
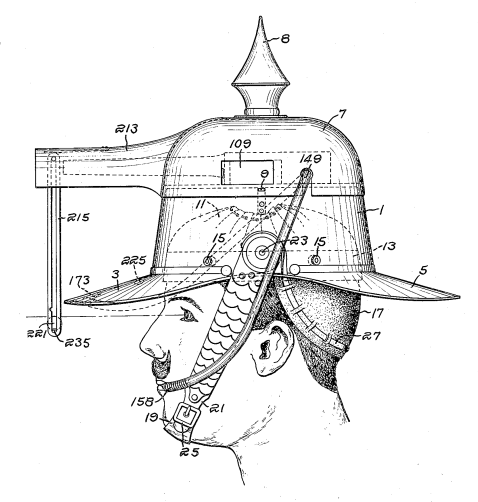
In 1915, Vermont inventor Albert Pratt proposed a new weapon: a head-mounted gun. You strap the helmet to your head and hold a hollow tube in your mouth; when you blow through the tube, the gun fires a bullet at whatever you’re looking at.
“The weapon described has many advantages,” Pratt writes confidently. “The gun is automatically aimed unconsciously and incidentally to the turning of the head of the marksman in the direction of the target. In self-protection, one immediately, instinctively turns the head in the direction of attack to see the enemy, or, in hunting, toward any sound made by nearby game. Thus the gun is automatically directed toward the mark in the course of the first instinctive movement. With the gun thus aimed, the only further operation necessary to fire the same is to blow through the tube and thereby expand the bulb and operate the trigger. This is accomplished entirely from the head of the marksman, leaving his hands and feet free further to defend himself or for other purposes as desired.”
“Under some circumstances the gun can be fired not only without the use of the hands and feet, but also without the use of the eyes of the marksman. For example, in hunting at night if an animal made a sound in underbrush, the head of the marksman would be instinctively turned in the direction of the sound and then the gun would be fired, without the use of the eyes of the marksman.”
If that’s not enough, Pratt also says that the helmet can be detached from its base and used as a cooking utensil. “The spike may be stuck in the ground to support the utensil or may be detached therefrom as desired.”